Coronary Artery Disease Survival Rate
Coronary artery disease survival rate. Factors affecting graft patency and survival Asian Cardiovasc Thorac Ann. Online ahead of print. There were 244 deaths after PCI and 211 after CABG hazard ratio HR 117.
95 confidence interval CI 097141. In the 11661 patients with MVD CABG was the initial therapy in 3782 PCI in 3540 and medical therapy in 4339. Patients with a MHR less than or equal to 150 beats min-1 and a LVEDP increase greater than or equal to 5 mmHg had a 6-yr survival of 56 - 12 in comparison to 92 -.
Survival rates were 48 28 18 and 9 for patients with single- double- triple- and left main artery disease respectively. 24 Chest pain symptoms and exercise electrocardiography are largely unhelpful for identifying those patients at risk. We conducted a multicenter study enrolling 4184 outpatients with stable CAD defined as previous myocardial infarction 1 year ago previous coronary revascularization 1 year ago andor 50 coronary stenosis by angiography.
Abnormalities documented by ventriculography were related to survival. Cardiac death occurred in 73 patients 369 and nonfatal cardiac events developed in 60 patients 309 during follow-up. The CASS registry has demonstrated that patients with a normal coronary morphology have an estimated 12 year survival rate of 91 in contrast to 74 in patients with 1 vessel disease VD 59 in 2-VD and 50 in 3-VD 1.
Risk-adjusted hazard ratios were calculated to compare different treatments. Coronary artery disease CAD is the leading cause of death in the United States. The 5- and 10-year survival rates were 807 and 642 respectively.
Cumulative 5-year survival was 914 with CABG 919 with PCI and 829 with medical therapy P. Survival in 2296 patients with peripheral arterial disease was compared with that of 13953 patients without peripheral arterial disease using Kaplan-Meier survival curves. One of the easiest risk scores which predict survival in CAD is based on the number of diseased vessels.
These results should be of VALUE IN ASSESSING THE PROGNOSIS OF NONSURGICALLY TREATED PATIENTS WITH CORONARY ARTERY DISEASE. Deaths due to noncoronary causes were uncommon 5 of total in the first 5 year period but were frequent 36 in the third period.
95 confidence interval CI 097141.
Risk-adjusted hazard ratios were calculated to compare different treatments. One of the easiest risk scores which predict survival in CAD is based on the number of diseased vessels. When cardiac death and nonfatal myocardial infarction MI were defined as. In addition the bypass surgery was associated with an overall 14-year increase in median survival time 77 vs. These results should be of VALUE IN ASSESSING THE PROGNOSIS OF NONSURGICALLY TREATED PATIENTS WITH CORONARY ARTERY DISEASE. Patients with a MHR less than or equal to 150 beats min-1 and a LVEDP increase greater than or equal to 5 mmHg had a 6-yr survival of 56 - 12 in comparison to 92 -. Survival rates were 48 28 18 and 9 for patients with single- double- triple- and left main artery disease respectively. Cumulative 5-year survival was 914 with CABG 919 with PCI and 829 with medical therapy P. 95 confidence interval CI 097141.
These results should be of VALUE IN ASSESSING THE PROGNOSIS OF NONSURGICALLY TREATED PATIENTS WITH CORONARY ARTERY DISEASE. The survival rate among patients in all three anatomic subgroups exceeded 90 at 5 years. Cumulative 5-year survival was 914 with CABG 919 with PCI and 829 with medical therapy P. Higher heart rate increases cardiac work load and oxygen demand and reduces coronary perfusion by decreasing the amount of time spent in diastole which in patients with obstructive coronary artery disease can trigger angina and myocardial infarction. The 5- and 10-year survival rates were 807 and 642 respectively. Clinical follow-up was performed after 2 years. Coronary artery disease CAD is the leading cause of death in the United States.



























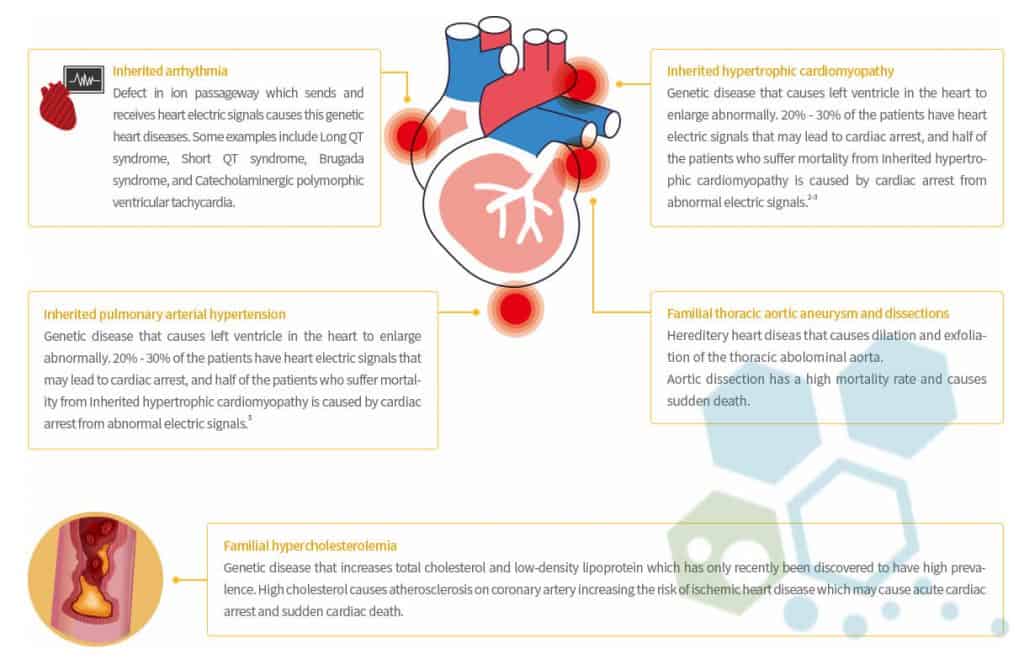
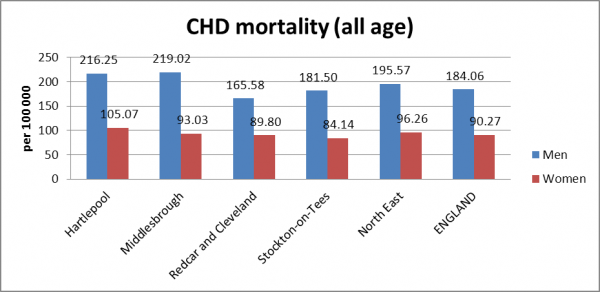
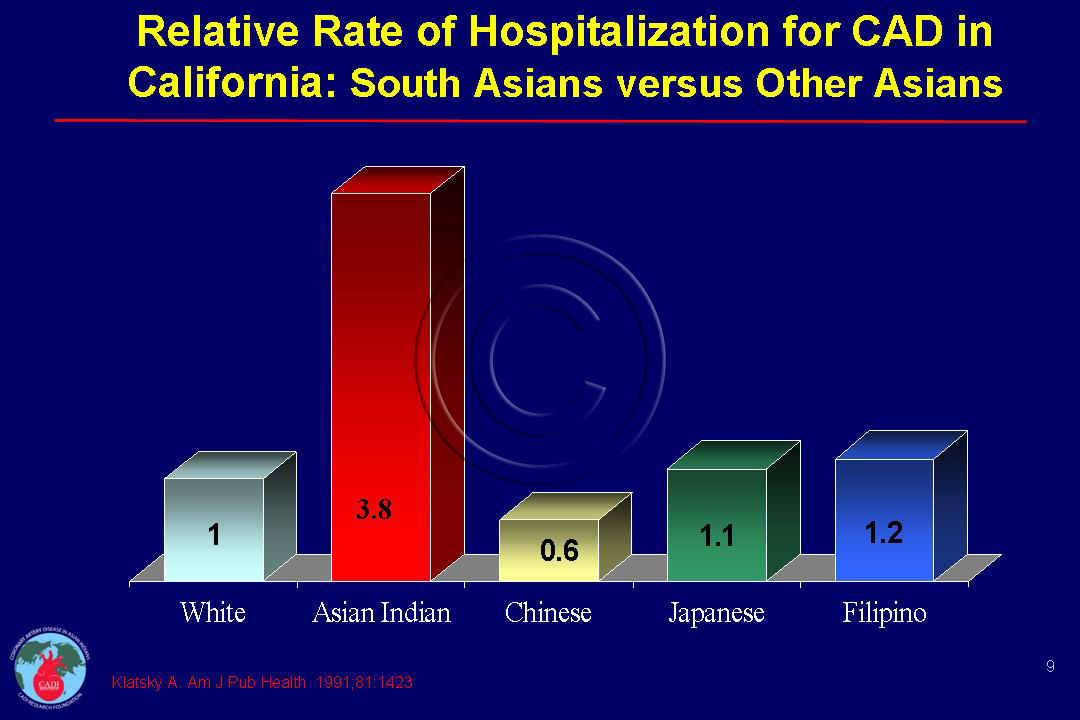
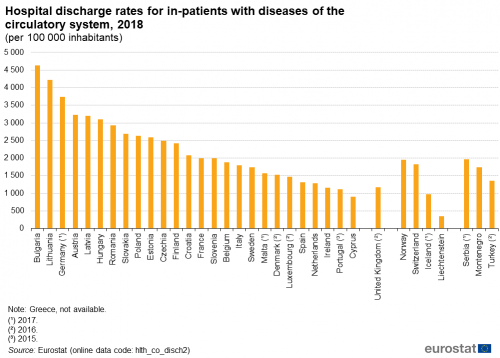


web-khoD--621x414@LiveMint.jpg)



Post a Comment for "Coronary Artery Disease Survival Rate"